INTRODUCTION
New Zealanders are famed for their friendliness and warmth towards overseas
visitors. New Zealand has a comparatively low cost of living, abundant fresh
food, and a variety of student accommodation options. Transport is
moderately priced and the country offers a safe and stable democratic
political environment with very low crime rates making it an excellent
environment in which to learn.
The eight institutions that make up the New Zealand university system are
located across the North and South Islands. New Zealand is also home to
several technical institutes and colleges.
New Zealand Education System
PRIMARY EDUCATION
Age 6 to 15 Years & Grade 1 to 9
From age 6 to 16, education is both compulsory and free. In an unusual
twist, people living over 5 kilometers from their nearest school may opt for
distance learning. Most children enter primary school at age 5 where they
remain for 6 years.
MIDDLE EDUCATION
Grade 10 to 13
The primary education program merges into middle school in different ways.
Children may remain on at their primary school for grades 7 and 8, or
complete these 2 years at bridging intermediate school (stream “A”).
Alternatively they may go directly on to junior secondary school where they
spend 4 years (stream “B”).
SECONDARY EDUCATION
Students who followed either version of stream “A” complete their last 5 years at secondary schools, while students of stream “B” spend their last 3 years at senior secondary school.
VOCATIONAL EDUCATION
This includes Industrial Training programs; the actual training is increasingly being provided in the workplace. Outputs include both apprenticeships for youth, and re-training for adults of all ages.
TERTIARY EDUCATION
This includes study at Universities, Polytechnics and Institutes of Technology, Private Training Institutions and Industry Training Organizations. Study for either academic or more practically focused qualifications, gaining everything from entry-level certificates to diplomas, degrees and doctorates.
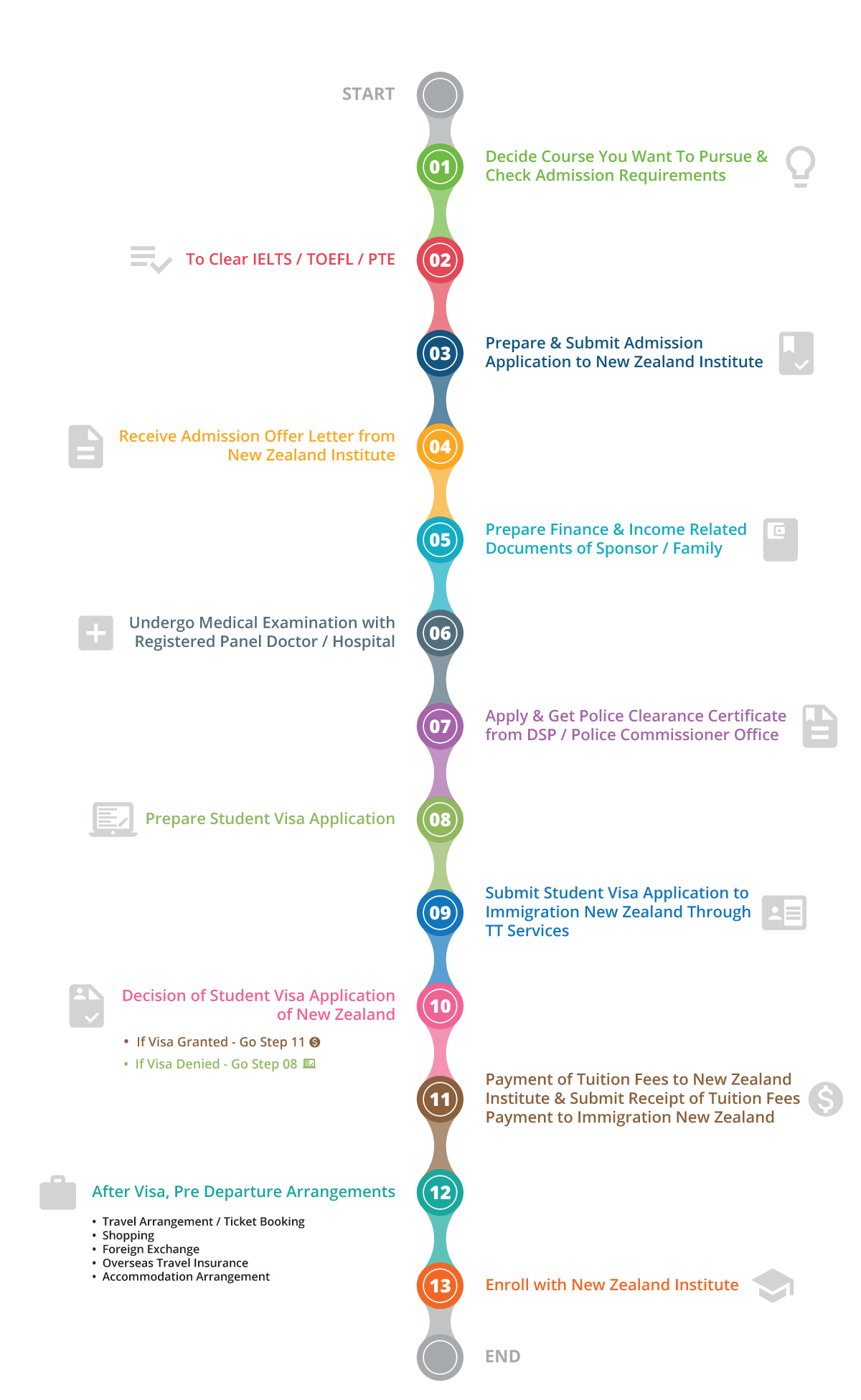
VISA PROCESS